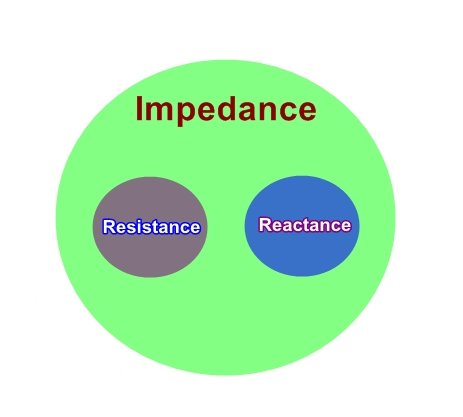
What is impedance
Impedance (Z) is similar to Resistance (R) . Impedance and Resistance both oppose the current in the circuit. Both are almost the same thing, But resistance related to DC Circuit. Resistance opposes the steady electric current in the DC circuit. Resistance remains the same (constant) at any different frequency range.
Impedance is related to the AC circuit. Impedance varies according to changing the frequency, this is not constant at different frequency ranges. Impedance also includes reactance (Inductive and capacitive property of the circuit).
Reactance
Reactance is the Resistance produced to AC Currents by Inductors and Capacitors only. This is a measure of the type of opposition to AC electricity due to capacitance or inductance.
The impedance is denoted by Z and unit of it is Ohm (Ω).
If the level of ohm is higher then the level impedance is also higher.
Impedance = Resistance + Reactance (Either inductive or Capacitive or both)
In DC circuit, Impedance is an effective Resistance of the circuit.
Z= R
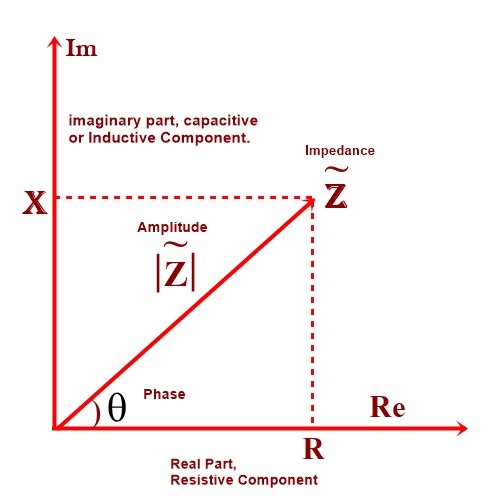
In AC circuits, it possesses both magnitude and phase, unlike resistance, which has only magnitude.
In the case of a capacitor, When the frequency increased then the resistance (Impedance) of the capacitor decreases. In Inductor this is just the opposite, When we increase the frequency range then Impedance increases in the inductor.
Impedance
Impedance is defined as a combination of resistance and reactance.
As we cannot assume any circuit with DC Current without Resistance, We cannot assume a circuit with AC current without Impedance.
Resistive Power– Energy burned by resistive power to Heat goes through that system,
In Reactive Power- the energy that goes to Antennas, Speakers, transmission lines, cables, etc represents how much energy is stored and propagated. Not burn to heat ie Impedance.
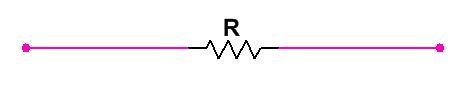
Resistance If there is Only Resistor is connected with Load in any circuit then is called Resistor.
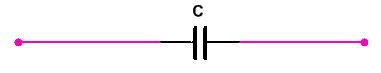
• Reactance If any circuit there is Only an inductor or capacitor connected with load. Then the value of v/I is called reactance.
In Reactance, There are 2 cases
(1) If the inductor in connected then in this case reactance is called inductive reactance,
and its value in scalar form XL = ѡL, and in vector form XL=JѡL Where ѡ=2Πf. Here If the frequency is increased then the value of wL is also increased.
(2) If Capacitor is connected then the Reactance is called Capacitive Reactance and it is denoted by (scalar form) Xc =
In vector form Where
If frequency (f) is increased then the value of Xc is decreased. ie ω inversely proportional to 2Πf.
♦ Impedance – If Any circuit consists of Resistance -Inductor. Or Resistance – Capacitor, Or Resistance-inductor-Capacitor. Then the value of v/I is called Impedance.
It is denoted by
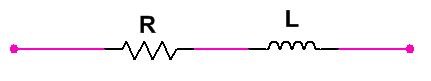
- If Resistor(R) and Inductor(L) are connected –The value of Impedance (scaler form)
In vector form Z= R+jωL
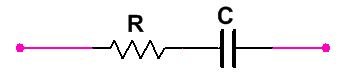
- If Resistor (R) and Capacitor(C) connected – Then
Impedance
And In vector form impedance
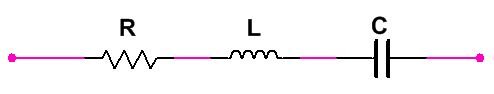
- If the Resistor (R), Inductor (L) capacitor (C) Connected – Then
Impedance
In vector form
Phasor Diagram of Impedance
FAQ – Impedance and Reactance
Q: What is impedance?
A: Impedance is the total opposition to the flow of alternating current (AC) in a circuit, comprising both resistance and reactance.
Q: How is impedance different from resistance?
A: While resistance refers to the opposition to current flow in a circuit due to the material properties of the conductors, impedance includes both resistance and the additional opposition caused by reactance.
Q: What causes reactance in a circuit?
A: Reactance is caused by the presence of inductors or capacitors in a circuit. Inductors exhibit inductive reactance (XL), while capacitors display capacitive reactance (XC).
Q: How is impedance calculated?
A: Impedance is calculated using complex numbers and can be found by combining resistance and reactance values. It is often represented by the formula Z = R + jX, where R is resistance, X is reactance, and j represents the imaginary unit.
Q: What are the units of impedance and reactance?
A: Impedance and reactance are measured in ohms (Ω), the same unit as resistance.
Q: Can impedance and reactance be negative?
A: Yes, impedance and reactance can be negative. Negative values indicate that the impedance or reactance has an opposite polarity or direction.
Q: How does impedance affect circuit behavior?
A: Impedance determines the relationship between voltage and current in a circuit. It influences the amount of current that can flow in the presence of a given voltage and affects the phase relationship between voltage and current.
Q: What is reactance?
A: Reactance is the opposition to the flow of alternating current (AC) in a circuit due to the presence of inductance or capacitance.
Q: What are the units of reactance?
A:Reactance is also measured in ohms (Ω).
Q: How is reactance represented in a circuit?
A: Reactance is denoted by the symbols XL (inductive reactance) and XC (capacitive reactance) for inductors and capacitors, respectively.
Q: What is the significance of reactance in AC circuits?
A: Reactance influences the behavior of AC circuits by introducing phase shifts between voltage and current and limiting the flow of current. It is particularly important in circuits with inductors or capacitors, where reactance plays a crucial role in determining circuit characteristics.
Q: How is reactance affected by frequency?
A: Reactance varies with frequency. Inductive reactance (XL) increases with frequency, while capacitive reactance (XC) decreases with frequency. The relationship is given by XL = 2πfL and XC = 1/(2πfC), where f is frequency, L is inductance, and C is capacitance.
Q: Can impedance and reactance be measured?
A: Yes, impedance and reactance can be measured using various techniques and instruments, such as impedance analyzers or network analyzers. These measurements help assess the behavior and characteristics of circuits and components.
Unit
- Impedance – Ω
- Reactance – Ω
- Resistance – Ω
Also Read
-
What is NOT Gate Logic
-
sample and Hold circuit
-
How does a capacitor block dc current
-
Logic gates
-
What is optocoupler
-
OP-amp Comparator


Thank you for this post. Its very inspiring.
very cool post, i actually enjoyed this web site, carry on it
Much interested have learnt alot from you
Carry on
It’s in reality a nice and useful piece of info. I’m glad that you just shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.