A diode is one of the most fundamental components in electronics, yet it plays a crucial role in how modern electronic systems function. To understand what is diode, it is best to think of it as a device that controls the direction of electric current. A diode allows current to flow easily in one direction while preventing it from flowing in the opposite direction. This unique one-way behavior is why a diode is often compared to an electrical check valve.
At its core, a diode is designed to manage and protect electrical circuits by controlling current flow. Without diodes, many electronic devices would be vulnerable to damage from unwanted or reverse currents. This makes understanding what is diode an essential first step for anyone beginning to learn electronics or electrical engineering.
Diodes are found in almost every electronic device we use daily, such as mobile phones, laptops, televisions, chargers, solar panels, and power supplies. Even though they are small and simple in structure, their function is critical to the safe and efficient operation of electronic systems. Because of their widespread use and importance, learning what is diode provides a strong foundation for understanding how electronic circuits work.
Definition of a Diode
A diode is a small electronic component with two terminals that is designed to control the flow of electric current. It is made from semiconductor material and works in a very specific way: it allows current to pass through it when connected in the correct direction, known as forward bias, and it blocks the current when connected in the opposite direction, known as reverse bias. This behavior helps protect electronic circuits and ensures electricity flows as intended.
In simple terms, understanding what is diode means understanding that it acts as a one-way path for electricity. When electricity tries to flow in the allowed direction, the diode opens the path and lets it pass. When electricity tries to flow in the wrong direction, the diode blocks the path and stops the flow completely.
Simple Definition
A diode lets electricity flow in one direction but stops it from flowing in the other direction.
You can think of a diode like a one-way door for electric current—it opens when current moves the right way and closes when the current tries to move backward. This simple but powerful function is why diodes are so important in electronic circuits.
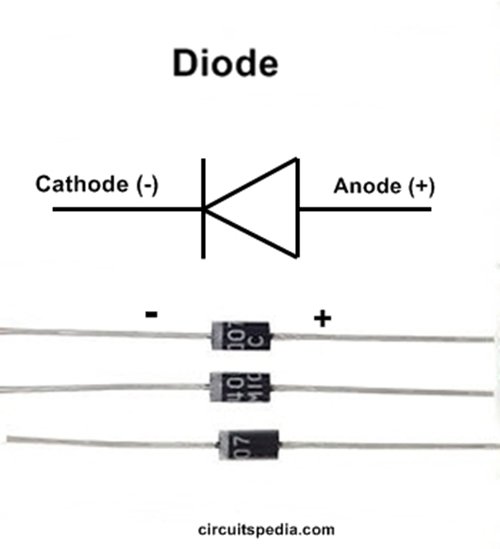
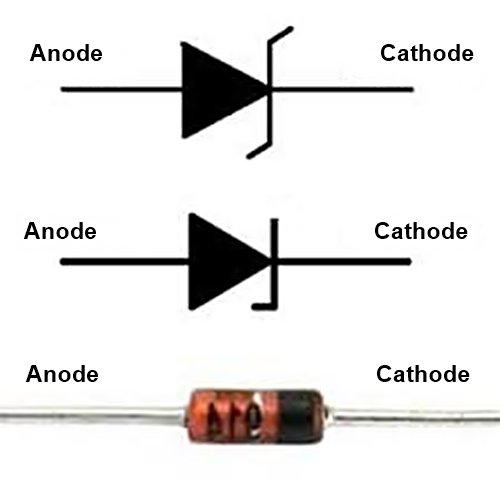
Symbol of a Diode
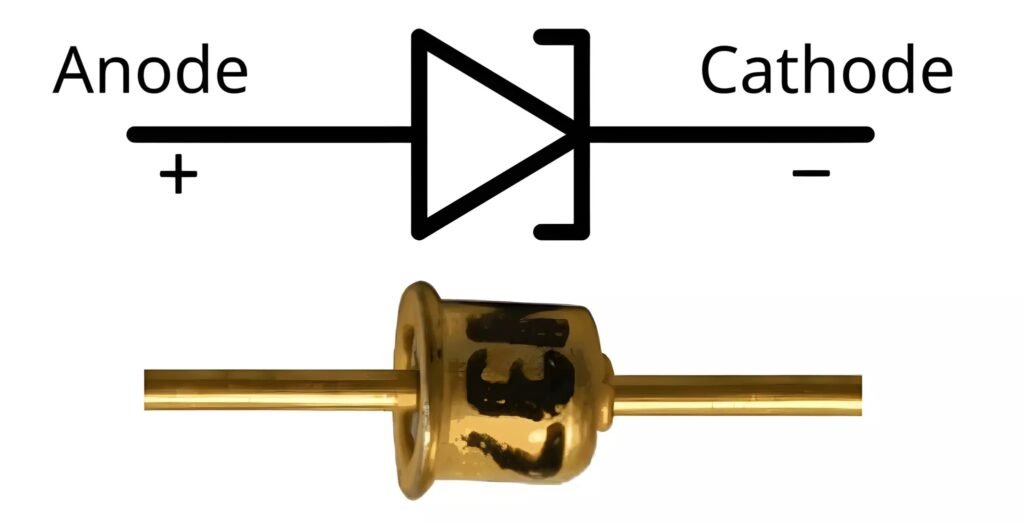
In electronic circuit diagrams, a diode is shown using a simple symbol made of two main parts: a triangle and a vertical line. This symbol helps engineers and beginners quickly understand how the diode will behave inside a circuit.
 Diode symbol
Diode symbol
The triangle in the diode symbol points in the direction where electric current is allowed to flow. It acts like an arrow, clearly showing the permitted path of current. When current moves in this direction, the diode allows it to pass.
The vertical line represents a barrier or stopping point. It shows the side where the diode blocks current. If current tries to flow toward this line from the wrong direction, the diode stops it and prevents any flow.
- In very simple terms, the diode symbol visually explains what is diode and how it works:
- The triangle says, “current can go this way.”
- The line says, “current cannot pass beyond this point.”
Because of this clear visual design, the diode symbol makes it easy to understand current direction in a circuit, even for complete beginners.
Terminals of a Diode
A diode has two terminals, and each terminal has a specific name and role. These terminals decide the direction in which electric current is allowed to flow.
1. Anode (A)
The anode is the positive side of the diode. This is the terminal where electric current enters the diode. When the anode is connected to the positive side of a power source, the diode becomes ready to allow current to flow.
In simple words, the anode is the entry point for current.
2. Cathode (K)
The cathode (K) is the negative side of the diode. This is the terminal where electric current leaves the diode after passing through it. The cathode acts like the exit point for current.
In simple words, the cathode is the exit point for current.
Direction of Current Flow
Electric current in a diode flows only in one direction:
from the Anode to the Cathode.
If current tries to flow from the cathode to the anode, the diode blocks it and no current flows. This one-direction rule is the key to understanding what is diode and why it is used in electronic circuits.
To make it even easier to remember:
- Anode → Cathode = Current flows
- Cathode → Anode = Current stops
This clear direction control is what makes a diode such an important and reliable electronic component.
How Does a Diode Work?
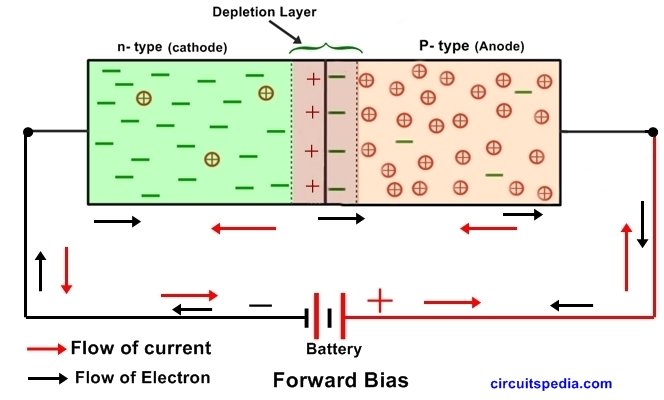
A diode is made using semiconductor material, most commonly silicon. This material gives the diode its special ability to control the direction of electric current. The way a diode behaves depends entirely on how it is connected in a circuit. There are two possible conditions: forward bias and reverse bias.
Forward Bias (Diode Allows Current)
In forward bias, the diode is connected in the correct direction:
- The anode is connected to the positive voltage
- The cathode is connected to the negative voltage
When connected this way, the diode conducts electricity. Current flows smoothly from the anode to the cathode, and the diode behaves like a closed switch that allows current to pass. This is the normal working condition of a diode when it is meant to let current flow.
In simple terms, forward bias means the diode is turned ON.
Reverse Bias (Diode Blocks Current)
In reverse bias, the diode is connected in the opposite direction:
- The anode is connected to the negative voltage
- The cathode is connected to the positive voltage
In this condition, the diode blocks electricity. No current is allowed to pass through the diode, and it behaves like an open switch. This protects the circuit by stopping unwanted or harmful current flow.
Why Diodes Are Important
Diodes are extremely important because they help electronic circuits work safely, correctly, and efficiently. Even though a diode is a small and simple component, it performs several critical functions that protect devices and control electrical behavior.
One of the main reasons diodes are important is that they protect circuits from damage. If electricity flows in the wrong direction, it can harm sensitive components. A diode blocks this unwanted reverse current and keeps the circuit safe.
Diodes are also used to convert AC to DC. Many electronic devices need direct current (DC) to operate, but the power coming from the mains supply is alternating current (AC). Diodes make this conversion possible by allowing current to flow in only one direction.
Another key role of diodes is to control voltage levels within a circuit. By managing how current moves, diodes help maintain stable and suitable voltage for different electronic components.
Diodes also prevent reverse current, which is especially important in power supplies, batteries, and charging systems. This prevents energy from flowing back into a source where it could cause overheating or failure.
Finally, diodes help improve efficiency in power systems by ensuring that electrical energy flows only where it is needed, reducing waste and unnecessary power loss.
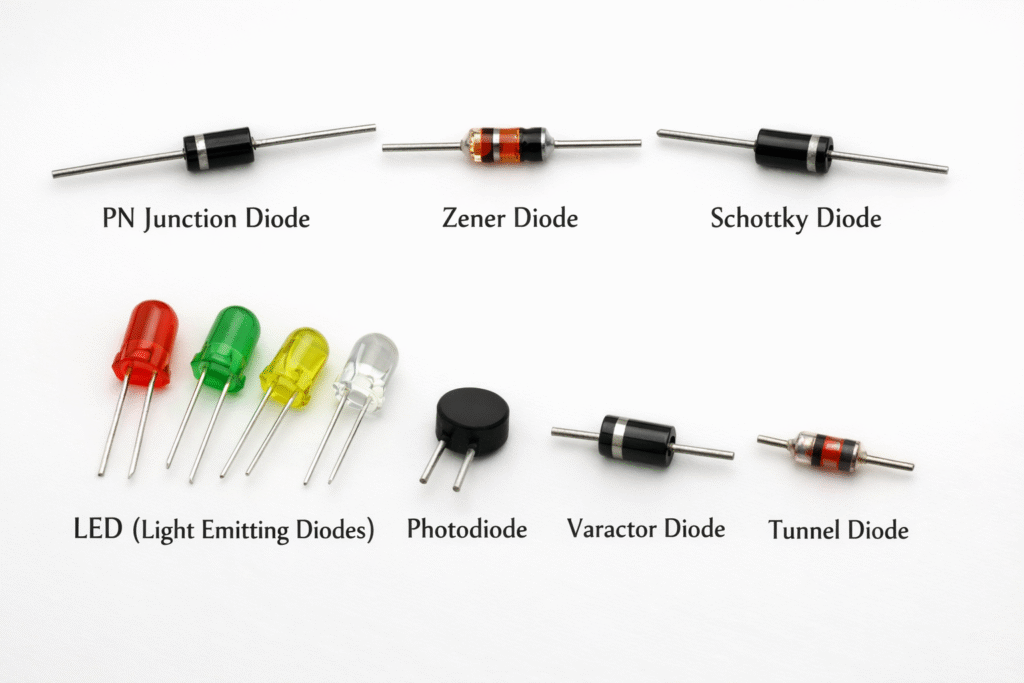
Types of Diodes
There are many types of diodes, and each one is designed to perform a specific job in an electronic circuit. Although all diodes control the direction of current, different types are optimized for different applications. Understanding these types makes it easier to grasp what is diode and how diodes are used in real devices.
1. PN Junction Diode
The PN junction diode is the most basic and commonly used type of diode. It is often the first diode beginners learn about.
- It allows current to flow in only one direction
- It is mainly used for rectification, which means converting AC into DC
- It is commonly found in power supplies and chargers
- This diode forms the foundation for understanding how all other diodes work.
2. Zener Diode
A Zener diode is specially designed to control and maintain voltage.
- It is used for voltage regulation
- Unlike normal diodes, it is designed to work safely in reverse bias
- It keeps voltage steady even if input voltage changes
- This makes Zener diodes very useful for protecting sensitive electronic components.
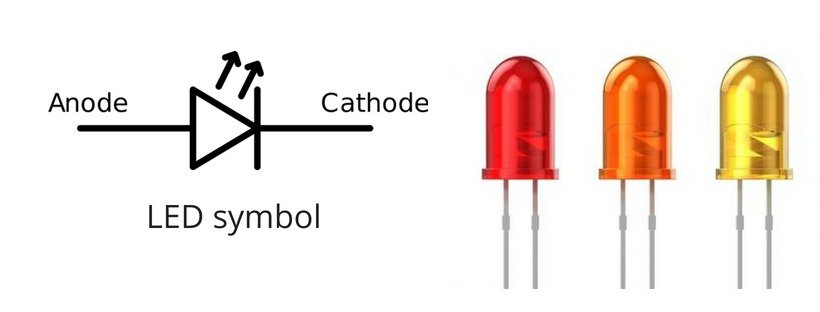
3. Light Emitting Diode (LED)
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces light when current flows through it.
- It converts electrical energy into visible light
- It is used in displays, bulbs, indicators, and screens
- It is energy-efficient and long-lasting
- LEDs are one of the most widely used diode types in everyday life.
4. Schottky Diode
A Schottky diode is known for its speed and efficiency.
- It switches ON and OFF very quickly
- It has a low voltage drop, meaning less power loss
- It is used in high-speed and high-frequency circuits
- This diode is ideal where fast operation is required.
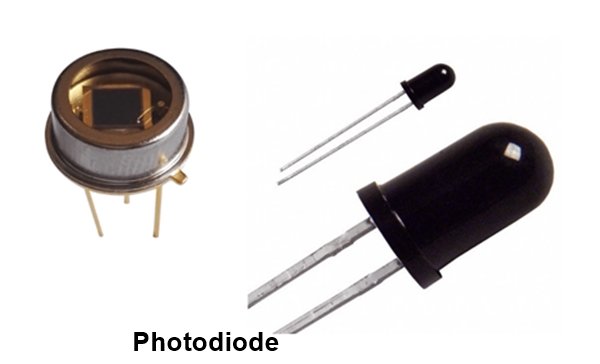
5. Photodiode
A photodiode works in the opposite way of an LED.
- It converts light into electrical current
- The amount of current depends on the light intensity
- It is used in light sensors, cameras, and solar-related devices
- Photodiodes are important wherever light detection is needed.
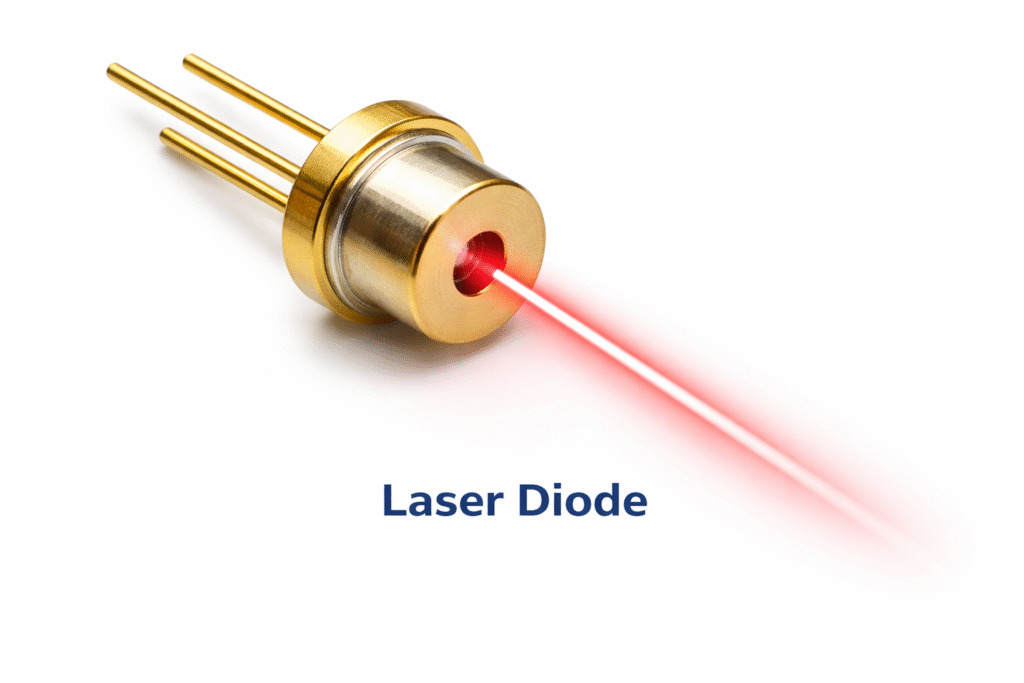
6. Laser Diode
A laser diode produces a strong, focused beam of light.
- It generates laser light, not normal light
- It is used in fiber optic communication, barcode scanners, and laser pointers
- It provides high precision and intensity
- Laser diodes are essential in modern communication and scanning technology.
7. Tunnel Diode
A tunnel diode is designed for very high-speed operation.
- It can operate at extremely fast speeds
- It is used in microwave and high-frequency applications
- It works using a special semiconductor effect
- Although less common, tunnel diodes are important in advanced electronic systems.
Diode as a Rectifier
One of the most common and practical uses of a diode is rectification. Many electronic devices cannot operate directly on alternating current (AC) because AC continuously changes direction. A diode solves this problem by allowing current to flow in only one direction, which makes it possible to convert AC into a usable form of direct current (DC). This function clearly explains what is diode and why it is essential in power-related circuits.
What Is Rectification?
Rectification is the process of converting AC (Alternating Current) into DC (Direct Current). In AC, the direction of current changes periodically, while in DC the current flows steadily in only one direction. Most electronic circuits require DC to work safely and reliably. A diode performs rectification by blocking the unwanted half of the AC cycle and allowing current to flow only in the desired direction, resulting in a DC output.
Types of Rectifiers
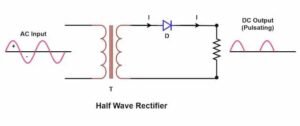
A half-wave rectifier is the simplest form of rectification. In this method, a single diode allows only one half of the AC cycle to pass while blocking the other half. Although this method is easy to understand and implement, it is not very efficient and is mostly used for basic learning or low-power applications.
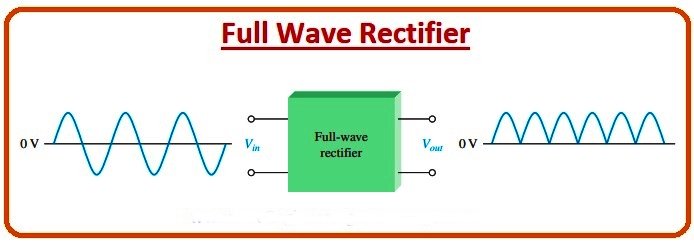
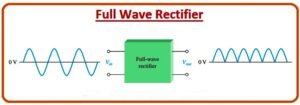
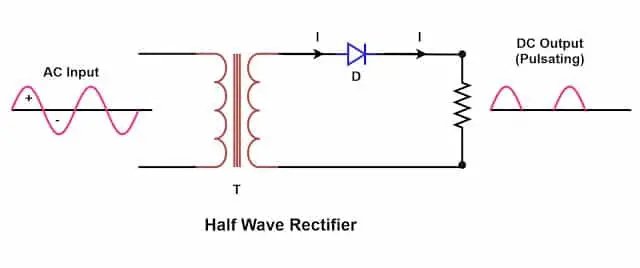 A full-wave rectifier improves efficiency by using both halves of the AC cycle. With the help of diodes, the negative half of the AC signal is converted into a positive output, resulting in smoother and more continuous DC compared to a half-wave rectifier. This type of rectification is commonly used where better performance is required.
A full-wave rectifier improves efficiency by using both halves of the AC cycle. With the help of diodes, the negative half of the AC signal is converted into a positive output, resulting in smoother and more continuous DC compared to a half-wave rectifier. This type of rectification is commonly used where better performance is required.
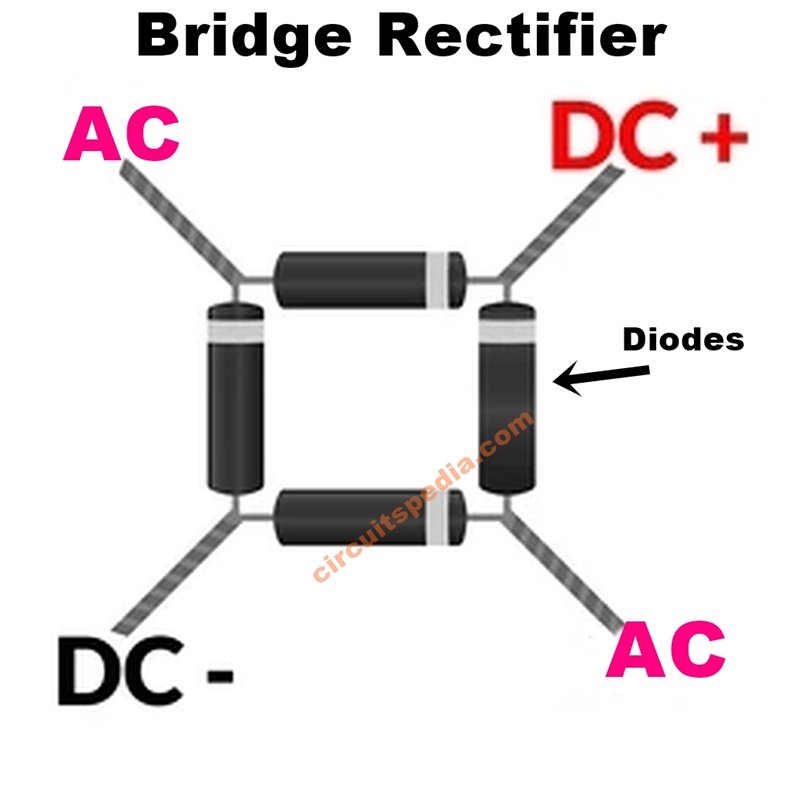
A bridge rectifier is a widely used rectifier circuit that uses four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration. It converts both halves of the AC cycle into DC without the need for a center-tapped transformer. Because of its efficiency and practicality, bridge rectifiers are commonly found in power supplies, adapters, and chargers.
Importance of Diodes in Rectifier Circuits
Diodes are essential in all rectifier circuits because they control the direction of current flow. Without diodes, AC power could not be converted into DC power. By acting as one-way gates for electricity, diodes make it possible for electronic devices to operate safely and efficiently, reinforcing the importance of understanding what is diode in basic electronics.
Voltage Drop in a Diode
When a diode allows current to flow through it, it does not behave like a perfect wire. Instead, it causes a small loss of voltage, known as the voltage drop. This voltage drop is a normal and unavoidable characteristic of a diode and occurs only when the diode is conducting current in forward bias. Understanding this behavior is an important part of learning what is diode and how it affects real circuits.
For a silicon diode, the voltage drop is typically about 0.7 volts. This means if 5 volts are applied to a circuit, only about 4.3 volts will be available after the diode. Germanium diodes have a lower voltage drop of around 0.3 volts, which makes them suitable for low-voltage applications. Schottky diodes have an even smaller voltage drop, usually around 0.2 volts, making them very efficient, where minimal power loss is required.
This voltage drop must always be considered when designing electronic circuits. If it is ignored, the output voltage may be lower than expected, which can cause circuits to behave incorrectly or fail to operate. In simple terms, a diode uses a small part of the voltage to function properly, and designers must account for this loss to ensure the circuit works safely and efficiently.
Advantages of Diodes
Diodes offer many advantages that make them one of the most widely used components in electronics. One of their biggest strengths is that they are simple and reliable. With no moving parts and a straightforward working principle, diodes perform their function consistently over long periods without frequent failure. This reliability is one of the key reasons they are trusted in critical electronic systems.
Another major advantage is their low cost. Diodes are inexpensive to manufacture, which helps keep the overall cost of electronic devices low. Despite their low price, they deliver highly effective performance, making them an excellent value component.
Diodes are also very small in size, which allows them to be easily used in compact and modern electronic devices such as smartphones and laptops.
In addition, diodes offer high efficiency by allowing current to flow only in the required direction and preventing unnecessary power loss. Many diodes are designed to operate efficiently even at high switching speeds. They also have a long operational life, as they are made from durable semiconductor materials that can function reliably for many years under normal conditions.
Disadvantages of Diodes
Despite their many benefits, diodes also have some limitations. One common disadvantage is their limited current capacity. Standard diodes can handle only a certain amount of current, and exceeding this limit can damage the device. For high-current applications, special power diodes are required.
Another drawback is heat generation at high current levels. When large currents pass through a diode, it can become hot due to power loss. If the heat is not properly managed, it may reduce performance or shorten the diode’s lifespan.
Finally, the voltage drop across a diode can reduce efficiency in some applications. Since a diode consumes a small amount of voltage when conducting, the output voltage becomes slightly lower than the input. In low-voltage or precision circuits, this voltage loss must be carefully considered during design.
In simple terms, understanding both the advantages and disadvantages helps explain what is diode and how to use it effectively in electronic circuits.
Conclusion
A diode is one of the most essential and widely used components in electronics. Its unique ability to allow electric current to flow in only one direction makes it a key element in power conversion, circuit protection, and signal control. Even though a diode is small and simple in structure, it performs a critical role in ensuring that electronic circuits operate safely and correctly.
Understanding what is diode helps build a strong foundation for learning electronics and electrical engineering. From basic power supplies to advanced technology systems, diodes are present almost everywhere. By learning how a diode works and why it is used, beginners take an important first step toward understanding how modern electronic devices function in everyday life.
Also read
- Diodes and their working in Hindi
- What is Thermistor
- What is Optocoupler
- Logic gates (AND, OR, NOT, NOR, NAND)