Audio amplifier circuit diagram
There are the following 3 types of best and easy Audio amplifier circuit diagrams
DIY audio amplifier
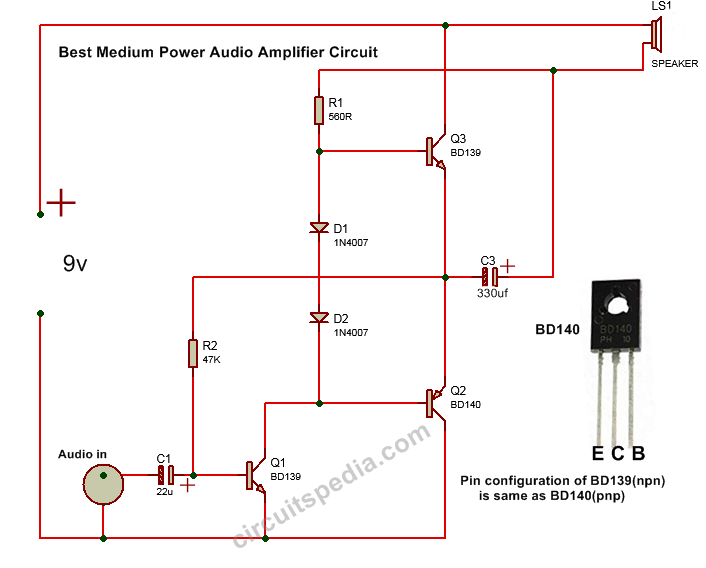
This is a Medium Power Audio Amplifier Circuit that operates on a 9V power supply and uses BD139 and BD140 transistors to amplify audio signals. Below is an explanation of the circuit connections and its working principle:
Circuit Components and Connections:
- Power Supply (9V)
- The circuit operates with a 9V DC power source.
- The positive terminal is connected to the collector of Q3 (BD139).
- The negative terminal (ground) is connected to the emitter of Q2 (BD140) and the negative side of C3.
- Audio Input Stage:
- The audio signal is fed through a capacitor C1 (22µF) to the base of Q1 (BD139, NPN transistor).
- The capacitor blocks DC components and allows AC signals (audio signals) to pass.
- Resistor R2 (47KΩ) acts as a biasing resistor for proper transistor operation.
- Amplification Stage (Q1, Q2, Q3):
- Q1 (BD139, NPN Transistor): Acts as a pre-amplifier, increasing the small audio signal.
- Q2 (BD140, PNP Transistor) and Q3 (BD139, NPN Transistor): Form a push-pull amplifier stage, boosting power output for the speaker.
- Biasing and Diodes:
- Diodes D1 and D2 (1N4007) provide thermal stabilization by maintaining a small voltage drop, ensuring proper transistor operation.
- Resistor R1 (560Ω) helps limit current to Q3.
- Output Stage:
- C3 (330µF Capacitor): Blocks DC voltage and allows only amplified AC (audio) signals to reach the speaker (LS1).
- The speaker is connected to the power supply and capacitor C3, receiving the amplified signal to produce sound.
Working Principle of the Circuit
- Audio Signal Input:
- The input audio signal is applied to the base of Q1 (BD139 NPN) through capacitor C1 (22µF).
- Q1 amplifies the weak audio signal.
- Push-Pull Operation (Class AB Amplifier):
- Q2 (BD140, PNP) and Q3 (BD139, NPN) work together in a push-pull configuration.
- Q2 conducts during the negative half-cycle, and Q3 conducts during the positive half-cycle of the signal.
- This reduces distortion and improves power efficiency.
- Output Amplification:
- The amplified audio signal is passed through C3 (330µF capacitor), which removes unwanted DC components.
- The clean AC signal drives the speaker, producing an amplified sound output.
Advantages of This Circuit:
✔ Simple design with few components.
✔ Operates on a 9V battery, making it portable.
✔ Good efficiency due to push-pull Class AB operation.
✔ Medium power output, suitable for small speaker applications.
Possible Modifications:
- Use a higher voltage power supply (12V or 15V) for more output power.
- Replace BD139/BD140 with TIP41/TIP42 for driving larger speakers.
- Add a heat sink to transistors for better heat dissipation.
Parts list
Resistors
560OHM-1, 47K-1
Transistors
BD139-2, Bd140-1
Capacitors
22uf25V-1, 330uf 25v-1
Diode 1N4007-2
———————————————————
Audio amplifier circuit diagram
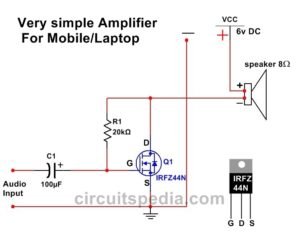
This is a Homemade Easy Stereo Amplifier Circuit, which uses IRFZ44N MOSFETs to amplify stereo audio signals for left (L) and right (R) channels. It operates on a 9V DC power supply and is designed to drive two small speakers.
Circuit Connections:
Power Supply (9V DC)
- The positive terminal (+9V) is connected to the drain (D) of Q1 and Q2 (IRFZ44N MOSFETs).
- The negative terminal (GND) is connected to the source (S) of both MOSFETs.
Input Stage (Audio Signals)
Left Channel (L) Input:
- The L audio signal is passed through C3 (220µF capacitor) to the gate (G) of Q1.
- R1 (22K–47KΩ resistor) provides biasing to stabilize the MOSFET operation.
Right Channel (R) Input:
- The R audio signal is passed through C1 (220µF capacitor) to the gate (G) of Q2.
- R2 (22K–47KΩ resistor) provides biasing.
Amplification Stage (MOSFETs)
- Q1 (IRFZ44N) amplifies the left channel, while Q2 (IRFZ44N) amplifies the right channel.
- These MOSFETs act as class A amplifiers, increasing the power of the incoming signals.
Output Stage (Speakers)
- The output signal is taken from the source (S) of each MOSFET.
- C4 (10µF capacitor) removes DC components, allowing only the amplified AC (audio) signal to pass to the speakers.
- Speakers (LS1 and LS2) receive the amplified audio signals and produce sound.
Working Principle:
- Audio Signal Input:
- The left and right channel audio signals enter through C3 and C1, respectively.
- These capacitors block any DC components and pass only AC signals (audio signals).
- MOSFET Amplification:
- The MOSFETs IRFZ44N amplify the weak signals from the input.
- R1 and R2 set the gate voltage for the MOSFETs, ensuring proper operation.
- The MOSFETs operate in a linear region, boosting the signal strength.
- Output to Speakers:
- The amplified signals are passed through C4 (10µF capacitor) to filter out DC components.
- The speakers receive the amplified audio signal, producing sound.
Advantages of This Circuit:
✔ Simple and low-cost stereo amplifier design.
✔ Uses MOSFETs (IRFZ44N), which provide better efficiency and power handling.
✔ Operates on a 9V battery, making it portable.
✔ Capacitors block DC to protect speakers from damage.
Possible Modifications:
- Use a higher voltage power supply (12V or 15V) for more output power.
- Increase capacitor values (e.g., C3 & C1 to 470µF) for better bass response.
- Add heat sinks to MOSFETs to prevent overheating.
- Include a pre-amplifier stage (e.g., using an op-amp or transistor) for better signal gain.
Parts list
capacitors
220uf 25V- 2, 10uf 25v -1
Resistor 22k-2
Mosfet IRFZ44N-2
———————————————————-
Audio amplifier circuit diagram
2-transistor audio amplifier
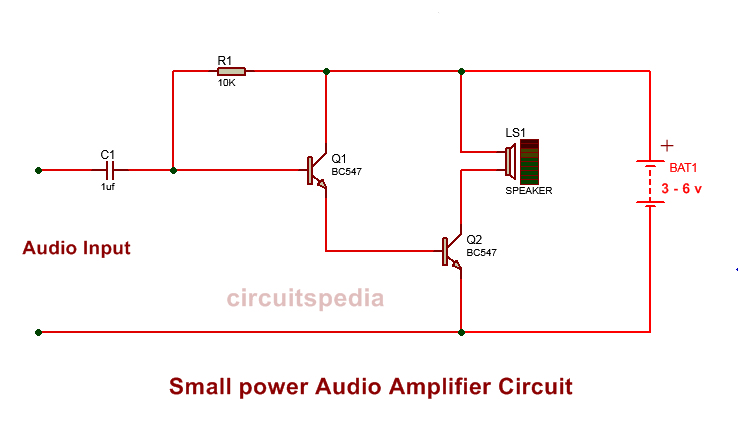
This is a Small Power Audio Amplifier Circuit that uses two BC547 NPN transistors to amplify an audio signal. It is powered by a 3V to 6V battery, making it suitable for small speaker applications such as headphone amplifiers or simple audio boosters.
Circuit Connections:
Power Supply (3V – 6V)
- The positive terminal of the battery is connected to the collector of Q1 (BC547).
- The negative terminal (ground) is connected to the emitter of Q2 (BC547).
Audio Input Stage
- The audio signal enters through C1 (1µF capacitor) to the base of Q1 (BC547).
- C1 blocks DC components and allows only AC signals (audio) to pass.
- R1 (10KΩ resistor) provides biasing to Q1, ensuring proper operation.
Amplification Stage (Q1 and Q2)
- Q1 (BC547) amplifies the weak audio signal received from the input.
- Q2 (BC547) acts as a current booster, providing enough power to drive the speaker.
Output Stage (Speaker)
- The collector of Q2 is connected to the speaker (LS1).
- The other terminal of the speaker is connected to the positive battery supply.
- The amplified signal drives the speaker, producing sound.
Working Principle:
-
Audio Signal Input:
- The input signal passes through C1, which removes DC components.
- Q1 amplifies the weak input signal, producing a higher voltage output.
-
Signal Boosting:
- The amplified signal from Q1 is fed into Q2.
- Q2 works as a current amplifier, increasing the current needed to drive the speaker.
-
Sound Output:
- The amplified signal is sent to the speaker (LS1).
- The speaker converts the electrical signal into sound.
Advantages of This Circuit:
✔ Simple design with minimal components.
✔ Works with a low-voltage battery (3V – 6V).
✔ Uses common BC547 transistors, which are easy to find.
✔ Suitable for small speaker applications.
Possible Modifications:
- Increase power supply voltage (e.g., 9V) for better output power.
- Use a higher-value capacitor (C1 = 4.7µF or 10µF) to improve bass response.
- Replace BC547 with a power transistor (e.g., BD139) for higher output power.
- Add a heat sink to Q2 for better heat dissipation.
Parts list
Resistor 10K-1
Capacitor 1uf 63v-1
Transistor BC547-2
Also read









Bro..kya mein aapke projects banake youTube mein share kar sakta hu…mera ek youTube channel hai..agar aap kaho to mein ye projects banake share krna chahta hu..i am waiting for u r reply
Plz reply