Wire size calculator
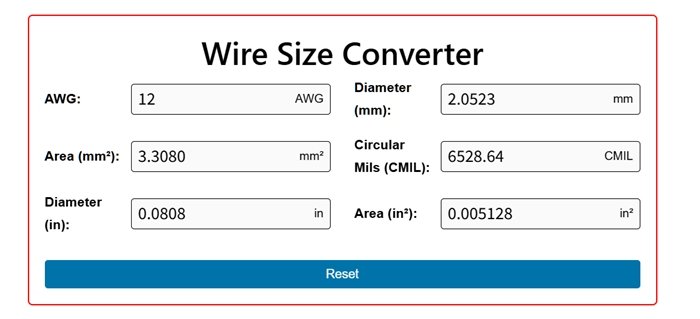
Wire Size Converter
Understanding Wire Size Conversion: AWG, mm, CMIL, and Inches
Choosing the correct wire size is crucial for the safety and efficiency of any electrical project, whether it’s wiring a house, building electronics, or working on automotive systems. Using a wire that is too small for the electrical current it carries can lead to overheating, voltage drops, and even fire hazards. Conversely, using an unnecessarily large wire can be costly and difficult to work with.
Wire sizes are specified using various standards around the world. In North America, the most common standard is the American Wire Gauge (AWG). However, in many other parts of the world, wire size is measured in metric units like millimeters (mm) for diameter or square millimeters (mm²) for cross-sectional area. Understanding how to convert between these units is essential for anyone working with electrical wire globally.
This article will demystify wire size conversion, explaining what AWG is, how wire size is measured, the key units involved (AWG, mm, CMIL, inches), and providing the essential conversion formulas you need.
What is American Wire Gauge (AWG)?
The American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a standardized wire gauge system used predominantly in the United States and Canada for the diameters of round, solid, nonferrous, electrically conducting wire. The system is counter-intuitive because as the AWG number increases, the wire diameter decreases. For example, a 12 AWG wire is thicker than a 14 AWG wire.
The AWG system is based on a geometric progression. There are 39 defined gauge sizes from 0000 (4/0) to 36 AWG. The ratio of the diameter of any gauge to the diameter of the next higher gauge is approximately constant. Specifically, the ratio of the diameter of AWG 0000 to AWG 36 is 92. Since there are 39 steps from 0000 to 36, the ratio of diameters between successive gauges is the 39th root of 92, which is approximately 1.1229.
Larger wire sizes beyond 0000 AWG are typically specified using kcmil (thousand circular mils) or MCM (an older term for thousand circular mils).
How is Wire Size Measured?
The most common ways to measure wire size are:
- Wire Gauge Tool: For AWG, a physical wire gauge tool is often used. This is a metal plate with slots or holes of different sizes. You find the slot or hole that the bare wire fits snugly into; the corresponding number on the tool indicates the AWG size.
- Caliper or Micrometer: For a more precise measurement, especially for metric sizes or when a gauge tool isn’t available, a caliper or micrometer can be used to measure the diameter of the bare wire conductor.
It’s important to measure only the metal conductor, not including any insulation or jacketing.
Wire Size Units: Diameter and Area
Wire size can be described by its diameter or its cross-sectional area.
- Diameter: The distance across the circular cross-section of the wire. Common units are inches (in) and millimeters (mm).
- Area: The size of the circular cross-section. A larger area means the wire can carry more current without excessive heat. Common units are square millimeters (mm²) and circular mils (CMIL).
What are Circular Mils (CMIL)?
A circular mil (CMIL) is a unit of area specifically used for the cross-sectional area of a wire with a circular cross-section. One circular mil is defined as the area of a circle with a diameter of one mil (where 1 mil = 0.001 inches).
The advantage of using circular mils is that the area in circular mils is simply the square of the diameter in mils. This avoids using in the calculation of the area from the diameter.
Area in CMIL = (Diameter in mils)
Since 1 inch = 1000 mils, Diameter in mils = Diameter in inches × 1000.
So, Area in CMIL = (Diameter in inches 1000)
Essential Wire Size Conversion Formulas
Here are the key formulas for converting between AWG, diameter in inches and mm, and area in circular mils and mm².
1. AWG to Diameter (Inches):
The diameter of an AWG wire can be calculated using the formula:
Where:
- is the diameter in inches
- is the AWG gauge number
For AWG sizes with multiple zeros (0, 00, 000, 0000), the values of are often taken as 0 AWG = 0, 00 AWG = -1, 000 AWG = -2, and 0000 AWG = -3 for use in this formula.
2. Diameter (Inches) to AWG:
Rearranging the above formula to find the AWG number from the diameter in inches:
Or using natural logarithm:
3. Diameter (Inches) to Diameter (mm):
Since 1 inch = 25.4 millimeters:
Where:
- is the diameter in millimeters
- is the diameter in inches
4. Diameter (mm) to Diameter (Inches):
5. Diameter (Inches) to Circular Mils (CMIL):
Where:
- is the area in Circular Mils
- is the diameter in inches
6. Circular Mils (CMIL) to Diameter (Inches):
7. Diameter (mm) to Area (mm²):
The area of a circle is
Where:
- is the area in square millimeters
- is the diameter in millimeters
8. Area (mm²) to Diameter (mm):
9. Circular Mils (CMIL) to Area (mm²):
You can convert CMIL to square inches first, then to mm².
square inches
1 square inch = (25.4 mm)2 square millimeters = 645.16 mm²
So,
. Area (mm²) to Circular Mils (CMIL):
Why Accurate Conversion Matters
Using a wire size converter and understanding these units and formulas is vital for several reasons:
- Safety: Ensuring the wire can handle the current load prevents overheating and fire.
- Performance: Correct wire size minimizes voltage drop, ensuring devices receive adequate power.
- Compliance: Electrical codes and standards often specify wire sizes in different units, requiring accurate conversion.
- Cost and Efficiency: Using the optimal wire size avoids unnecessary material costs and makes installation easier.
By utilizing a reliable wire size converter and understanding the underlying principles, you can confidently select the right wire for your electrical applications, ensuring safety and optimal performance.
More tools
- Watt to ampere converter | Power to current conversion
- SMD Resistor code calculator
- Capacitor series and parallel calculator
- 555 Timer calculator (Astable and Monostable