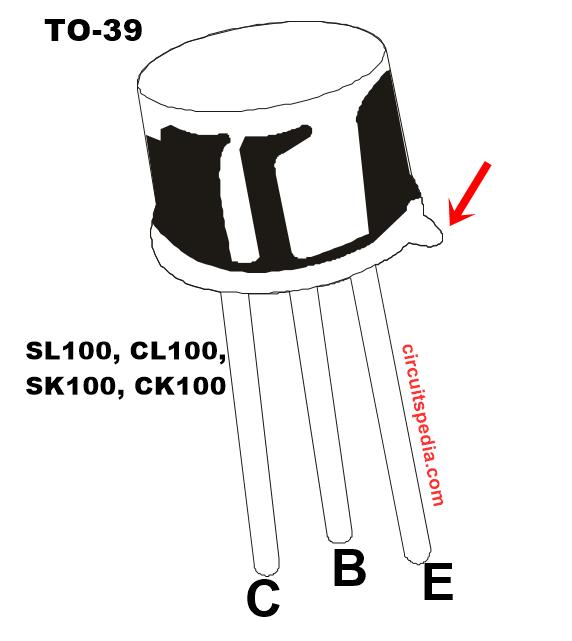
The SL100 is a general purpose medium power NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) bipolar junction transistor (BJT) commonly used in various electronic circuits for amplification and switching purposes. SL100 transistor current rating is 500ma.
SL100 Specifications
- Transistor Material : Si
- Polarity type : NPN
- Collector-Emitter (VCEO) voltage : 50V
- Collector Base (VCBO) voltage : 60V
- Collector Current (Ic): 0.5A (500ma)
- The saturation voltage from Collector to Emitter : 0.6V
- Output Capacitance : 20pf
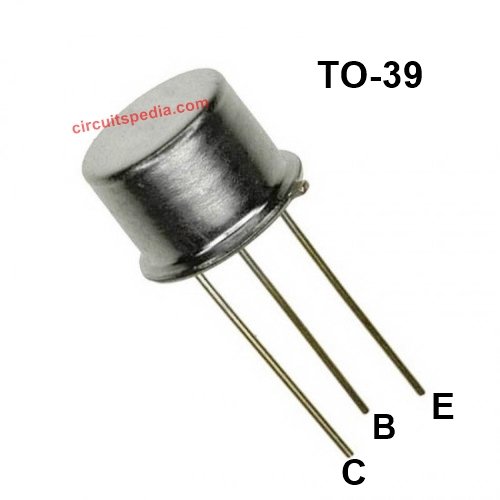
- Package : TO-39
- DC Current gain (hfe) : 100 to 300
- Emitter Base (VEBO) voltage : 5.0V
- Dissipation of Collector Power (Max) : 0.8 W
- The saturation voltage from Base to Emitter : 1.3V
- Operating and Storage Temperature : -65℃ to 200℃
How It Works :
- Amplification: In an amplifier configuration, a small input current to the base controls a larger current flow between the collector and emitter, thus amplifying the input signal.
- Switching: In a switching application, the transistor can turn on or off the flow of current between the collector and emitter based on the base current, acting like a switch
Applications of SL100 transistor
Switching Applications:
- Used in low-power switching circuits.
- Acts as an on/off switch for controlling loads like LEDs, relays, and other small electronic components.
Amplification Applications:
- Employed in audio amplification circuits.
- Used in signal amplification circuits to boost weak signals.
Oscillator Circuits:
- Utilized in generating periodic signals or oscillations.
- Found in applications such as signal generators and timing circuits.
Signal Processing:
- Used in various signal processing applications to modulate, demodulate, or process analog signals.
Motor Control:
- Can be used to control small motors by switching them on and off.
Features of SL100 Transistor
- High Current Gain:
-
- Provides a high DC current gain, making it suitable for amplification purposes.
- Low Saturation Voltage:
-
- Offers low saturation voltage, ensuring efficient switching with minimal power loss.
- High Power Dissipation:
-
- Capable of dissipating up to 800mW, making it suitable for moderate power applications.
- Wide Operating Frequency:
-
- Can operate at high frequencies, making it suitable for high-frequency signal processing applications.
- Robust Construction:
-
- Packaged in a TO-39 metal can package, providing durability and better heat dissipation.
Typical Circuit Configuration
Common-Emitter Amplifier:
- Components:
- Resistors for biasing the transistor.
- Capacitors for coupling and bypassing.
- SL100 transistor.
- Function:
- A small input signal is applied to the base.
- The transistor amplifies the signal and outputs a larger signal at the collector.
Switching Circuit:
- Components:
- SL100 transistor.
- Resistors for base current limiting.
- Load (e.g., LED, motor).
- Function:
- A control signal is applied to the base.
- The transistor switches the load on or off depending on the base signal.
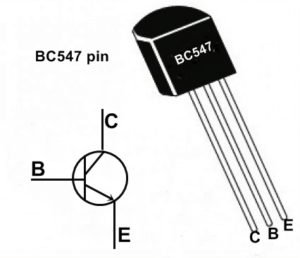
SL100 transistor vs BC547
The SL100 and BC547 are both NPN transistors commonly used in various electronic circuits, but they have different specifications and applications. Here’s a comparison between the two:
SL100
- Type: NPN
- Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): 45V
- Maximum Collector Current (Ic): 500mA
- Maximum Power Dissipation (Ptot): 0.8W
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 20 to 300
- Package: TO-39 metal can
BC547
- Type: NPN
- Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): 45V
- Maximum Collector Current (Ic): 100mA
- Maximum Power Dissipation (Ptot): 500mW
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 110 to 800
- Package: TO-92 plastic package
Key Differences
- Current Handling:
- The SL100 can handle a higher collector current (500mA) compared to the BC547 (100mA), making the SL100 more suitable for applications requiring higher current.
- Power Dissipation:
- The SL100 has a higher maximum power dissipation (1.8W) compared to the BC547 (500mW), indicating it can manage more power without overheating.
- Gain:
- The BC547 typically has a higher range of current gain (hFE), which can be beneficial in low current amplification applications.
- Package Type:
- The SL100 comes in a TO-39 metal can package, which can offer better heat dissipation, while the BC547 comes in a TO-92 plastic package, which is smaller and more suitable for compact circuits.
Applications
- SL100: Due to its higher current and power handling capabilities, the SL100 is often used in power amplification circuits, switching applications, and general-purpose high current applications.
- BC547: The BC547, with its higher current gain and lower current handling, is typically used in low current amplification, signal processing, and switching applications in low-power devices.
SL100 Datasheet